У цьому уроці ви дізнаєтесь, як працює алгоритм Прима. Крім того, ви знайдете робочі приклади алгоритму Prim у C, C ++, Java та Python.
Алгоритм Прима - це мінімальний алгоритм охоплюючого дерева, який приймає графік як вхідний і знаходить підмножину ребер цього графіка, який
- сформуйте дерево, яке включає кожну вершину
- має мінімальну суму ваг серед усіх дерев, які можна сформувати з графіка
Як працює алгоритм Прима
Це підпадає під клас алгоритмів, які називаються жадібними алгоритмами, які знаходять локальний оптимум в надії знайти загальний оптимум.
Ми починаємо з однієї вершини і продовжуємо додавати ребра з найменшою вагою, поки не досягнемо своєї мети.
Етапи реалізації алгоритму Prim такі:
- Ініціалізуйте мінімальне дерево, що охоплює, вершиною, вибраною навмання.
- Знайдіть усі ребра, що з’єднують дерево з новими вершинами, знайдіть мінімум і додайте його до дерева
- Повторюйте крок 2, поки не отримаємо мінімальне дерево, що охоплює
Приклад алгоритму Прима
 Почніть з виваженим графом
Почніть з виваженим графом  Виберіть вершину
Виберіть вершину  Виберіть найкоротший край від цієї вершини і додати його
Виберіть найкоротший край від цієї вершини і додати його  вибрати найближчу вершину ще не в рішенні
вибрати найближчу вершину ще не в рішенні  Виберіть найближчий край ще не в розчині, якщо є кілька варіантів, вибрати один в довільному порядку
Виберіть найближчий край ще не в розчині, якщо є кілька варіантів, вибрати один в довільному порядку 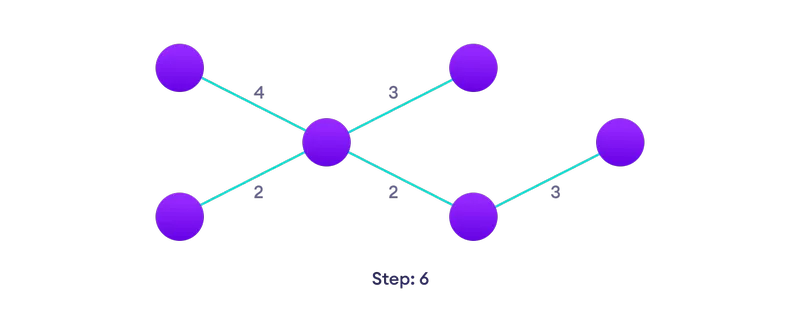 Повторюйте , поки мати обшивне дерево
Повторюйте , поки мати обшивне дерево
Псевдокод Алгоритму Прима
Псевдокод алгоритму prim показує, як ми створюємо два набори вершин U і VU. U містить список вершин, які були відвідані, а VU - список вершин, які не були. По черзі ми переміщуємо вершини з множини VU до множини U, з'єднуючи край найменшої ваги.
T = ∅; U = ( 1 ); while (U ≠ V) let (u, v) be the lowest cost edge such that u ∈ U and v ∈ V - U; T = T ∪ ((u, v)) U = U ∪ (v)
Приклади Python, Java та C / C ++
Хоча використовується матричне представлення графіків суміжності, цей алгоритм також може бути реалізований за допомогою Списку суміжності для підвищення його ефективності.
Python Java C C ++ # Prim's Algorithm in Python INF = 9999999 # number of vertices in graph V = 5 # create a 2d array of size 5x5 # for adjacency matrix to represent graph G = ((0, 9, 75, 0, 0), (9, 0, 95, 19, 42), (75, 95, 0, 51, 66), (0, 19, 51, 0, 31), (0, 42, 66, 31, 0)) # create a array to track selected vertex # selected will become true otherwise false selected = (0, 0, 0, 0, 0) # set number of edge to 0 no_edge = 0 # the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be # always less than(V - 1), where V is number of vertices in # graph # choose 0th vertex and make it true selected(0) = True # print for edge and weight print("Edge : Weight") while (no_edge G(i)(j): minimum = G(i)(j) x = i y = j print(str(x) + "-" + str(y) + ":" + str(G(x)(y))) selected(y) = True no_edge += 1
// Prim's Algorithm in Java import java.util.Arrays; class PGraph ( public void Prim(int G()(), int V) ( int INF = 9999999; int no_edge; // number of edge // create a array to track selected vertex // selected will become true otherwise false boolean() selected = new boolean(V); // set selected false initially Arrays.fill(selected, false); // set number of edge to 0 no_edge = 0; // the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be // always less than (V -1), where V is number of vertices in // graph // choose 0th vertex and make it true selected(0) = true; // print for edge and weight System.out.println("Edge : Weight"); while (no_edge < V - 1) ( // For every vertex in the set S, find the all adjacent vertices // , calculate the distance from the vertex selected at step 1. // if the vertex is already in the set S, discard it otherwise // choose another vertex nearest to selected vertex at step 1. int min = INF; int x = 0; // row number int y = 0; // col number for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) ( if (selected(i) == true) ( for (int j = 0; j G(i)(j)) ( min = G(i)(j); x = i; y = j; ) ) ) ) ) System.out.println(x + " - " + y + " : " + G(x)(y)); selected(y) = true; no_edge++; ) ) public static void main(String() args) ( PGraph g = new PGraph(); // number of vertices in grapj int V = 5; // create a 2d array of size 5x5 // for adjacency matrix to represent graph int()() G = ( ( 0, 9, 75, 0, 0 ), ( 9, 0, 95, 19, 42 ), ( 75, 95, 0, 51, 66 ), ( 0, 19, 51, 0, 31 ), ( 0, 42, 66, 31, 0 ) ); g.Prim(G, V); ) )
// Prim's Algorithm in C #include #include #define INF 9999999 // number of vertices in graph #define V 5 // create a 2d array of size 5x5 //for adjacency matrix to represent graph int G(V)(V) = ( (0, 9, 75, 0, 0), (9, 0, 95, 19, 42), (75, 95, 0, 51, 66), (0, 19, 51, 0, 31), (0, 42, 66, 31, 0)); int main() ( int no_edge; // number of edge // create a array to track selected vertex // selected will become true otherwise false int selected(V); // set selected false initially memset(selected, false, sizeof(selected)); // set number of edge to 0 no_edge = 0; // the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be // always less than (V -1), where V is number of vertices in //graph // choose 0th vertex and make it true selected(0) = true; int x; // row number int y; // col number // print for edge and weight printf("Edge : Weight"); while (no_edge < V - 1) ( //For every vertex in the set S, find the all adjacent vertices // , calculate the distance from the vertex selected at step 1. // if the vertex is already in the set S, discard it otherwise //choose another vertex nearest to selected vertex at step 1. int min = INF; x = 0; y = 0; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) ( if (selected(i)) ( for (int j = 0; j G(i)(j)) ( min = G(i)(j); x = i; y = j; ) ) ) ) ) printf("%d - %d : %d", x, y, G(x)(y)); selected(y) = true; no_edge++; ) return 0; )
// Prim's Algorithm in C++ #include #include using namespace std; #define INF 9999999 // number of vertices in grapj #define V 5 // create a 2d array of size 5x5 //for adjacency matrix to represent graph int G(V)(V) = ( (0, 9, 75, 0, 0), (9, 0, 95, 19, 42), (75, 95, 0, 51, 66), (0, 19, 51, 0, 31), (0, 42, 66, 31, 0)); int main() ( int no_edge; // number of edge // create a array to track selected vertex // selected will become true otherwise false int selected(V); // set selected false initially memset(selected, false, sizeof(selected)); // set number of edge to 0 no_edge = 0; // the number of egde in minimum spanning tree will be // always less than (V -1), where V is number of vertices in //graph // choose 0th vertex and make it true selected(0) = true; int x; // row number int y; // col number // print for edge and weight cout << "Edge" << " : " << "Weight"; cout << endl; while (no_edge < V - 1) ( //For every vertex in the set S, find the all adjacent vertices // , calculate the distance from the vertex selected at step 1. // if the vertex is already in the set S, discard it otherwise //choose another vertex nearest to selected vertex at step 1. int min = INF; x = 0; y = 0; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) ( if (selected(i)) ( for (int j = 0; j G(i)(j)) ( min = G(i)(j); x = i; y = j; ) ) ) ) ) cout << x << " - " << y << " : " << G(x)(y); cout << endl; selected(y) = true; no_edge++; ) return 0; )
Алгоритм Прима проти Крускала
Алгоритм Крускала - ще один популярний мінімальний алгоритм охоплюючого дерева, який використовує іншу логіку для пошуку MST графіка. Замість того, щоб починати з вершини, алгоритм Крускала сортує всі ребра від малої ваги до великої і продовжує додавати найнижчі ребра, ігноруючи ті ребра, які створюють цикл.
Складність алгоритму Прима
Складність часу алгоритму Прима становить O(E log V).
Застосування алгоритму Прима
- Прокладка кабелів електропроводки
- У мережі розроблений
- Створювати протоколи в мережевих циклах








